
Knee Pain
The knee joint connects the thigh to the lower leg and bears the body’s weight during movement. Its balance between mobility and stability is crucial, and any disturbance in this balance can lead to pain, stiffness, or injury.
The knee is one of the most heavily used joints in the body, absorbing impact with every step, squat, and jump. Overuse, sudden directional changes, poor alignment, or weakness in supporting muscles can overload the joint structures, leading to pain, swelling, or instability. Knee pain may develop gradually or appear suddenly and can worsen with activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or prolonged sitting.
Common Conditions
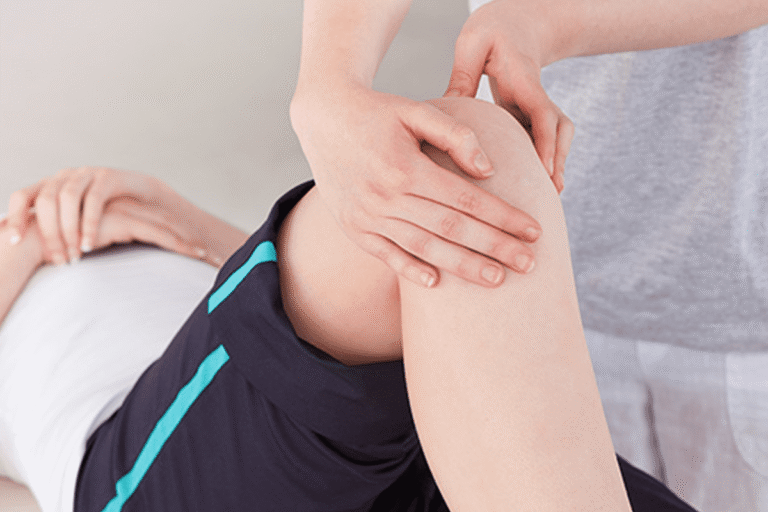
Knee osteoarthritis(OA) is not just a knee problem; from an osteopathic perspective, it reflects imbalances in joint mechanics, muscle strength, posture, gait, and load distribution, often involving the hip, ankle, pelvis, and spine.
Osteopathy view of treatment on OA knee
At Institute of Physical & Mental Health (IPMH), we *focus on treating the root cause, not just knee pain*. By-
- Improving knee joint mobility
- Reduces pain and stiffness
- Releases tight muscles and fascia with specific myofascial techniques
- Enhances function and Strengthen week muscles with functional electrical Stimulator(FES)
- Corrects misalignment and gait patterns
- Promotes long-term relief and quality of life
What an ACL Injury Really Affects:
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) stabilizes knee joint motion and contributes to joint position sense (proprioception) — critical for balance and coordinated movement. After injury, loss of mechanoreceptors can reduce proprioceptive ability and dynamic stability.
ACL injury often impairs neuromuscular control, balance, and movement patterns, not just passive tissue integrity.
How osteopaths treat and support ACL recovery.
Holistic Assessment: We check knee alignment, gait, muscle balance and movement mechanics.
Myofascial techniques: Gentle tissue release and joint mobilization reduce pain and improve mobility.
Strength & Proprioception Training: Targeted exercises; Rebuilding stability with high power *Pulse Magneto Electric Field* , balance and neuromuscular control with Functional Electrical Stimulator(FES)
- Root-cause focused, not symptom masking
- Safe, non-invasive, evidence-based techniques
- Combines structural, functional & lifestyle care
- Helps reduce pain, improve mobility & prevent recurrence
Root-cause focused, not symptom masking
Myofascial techniques: Gentle tissue release and joint mobilization reduce pain and improve mobility.
Strength & Proprioception Training:
Targeted exercises: Rebuilding stability with high power *Pulse Magneto Electric Field* , balance and neuromuscular control with Functional Electrical Stimulator(FES)
Why IPMH’s Osteopathic Approach Works
Fractures and traumatic injuries heal not only by bone union, but by restoring joint mobility, muscle function, circulation, and coordinated movement. Prolonged immobilization often leads to stiffness, muscle weakness, fascial tightness, and altered posture, which must be addressed for complete recovery.
Healing beyond bones; Restoring movement; Rebuilding confidence..
🌿 Osteopathic Post-Fracture Care
At IPMH, osteopathy supports natural healing and functional recovery, beyond fracture repair.
- Root-cause focused, not symptom masking
- Safe, non-invasive, evidence-based techniques
- Combines structural, functional & lifestyle care
- Helps reduce pain, improve mobility & prevent recurrence
- Releases fascial tightness from immobilization
- Corrects posture & gait patterns
🌀 *Role of Myofascial Decompression (Cupping Therapy) in Post-Fracture.
- Reduces pain, swelling & stiffness
- Restores joint mobility after cast or surgery
- Improves muscle strength & coordination
- Releases fascial tightness from immobilization
like patellar or quadriceps tendinopathy are not simply tendon inflammation but overuse-related tendon disorders involving degenerative changes, abnormal load distribution, and muscle imbalance around the knee and lower limb. Effective recovery involves addressing these underlying biomechanical factors through manual therapy, movement correction, and progressive tendon loading rather than only symptom relief. Osteopathic treatment uses hands-on techniques such as soft tissue work, myofascial release, and joint mobilisation to reduce pain, improve circulation and flexibility, and restore alignment; this is combined with individualised exercise and load-management strategies that strengthen surrounding muscles, correct gait and posture, and enhance neuromuscular control to support tendon resilience and long-term function.
Not Just Front Knee Pain. Patellofemoral disorder involves more than kneecap discomfort — it often results from poor patellar tracking, muscle imbalance, and altered lower-limb biomechanics Problems like weak quadriceps (especially VMO), tight lateral muscles, and abnormal movement patterns can cause the kneecap to track improperly, increasing joint stress and pain during activities like stair climbing or squatting.
Osteopathic Approach
- Relieves anterior knee pain and stiffness
- Improves patellar tracking and joint mobility
- Releases tight muscles and fascial tension
- Corrects posture and movement patterns
- Strengthens supportive muscles for better control
- Prevents recurrence and improves daily function
Balanced movement. Pain-free knees.
The meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous structure that plays a key role in shock absorption, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception in the knee. Injury disrupts these functions and alters knee mechanics, increasing joint stress and movement dysfunction in the knee, hip, ankle and pelvis. Untreated imbalance can lead to stiffness, altered gait and long-term degeneration.
🧠 Osteopathy vs. Surgery
Not all meniscus injuries require surgery. Many small and degenerative tears can respond well to conservative rehabilitation focused on mobility, strength and mechanics. Evidence suggests that non-operative management often matches surgical outcomes in such cases and avoids surgery-related risks, especially when mechanical symptoms are absent.
🌿How does Osteopathy and advance technologies help in Meniscus Injury Recovery
- Class IV Laser Therapy: Promotes tissue healing by improving cellular metabolism, reducing inflammation, and accelerating cartilage and soft-tissue repair.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Activates and strengthens weak muscles (especially quadriceps), improves neuromuscular control, and supports knee stability during recovery.
- Movement Retraining: Corrects gait, posture, and lower-limb biomechanics to prevent recurrence.
Knee bursitis is not simply swelling of a fluid-filled sac; from an osteopathic perspective, it commonly develops due to repetitive stress, poor biomechanics, muscle tightness, altered posture, and faulty movement patterns that overload the knee and surrounding tissues. osteopaths focuses on removing the source of irritation, not just calming inflammation, by improving joint mobility, releasing tight muscles and fascia, correcting posture and movement stress, and supporting natural healing. This approach helps reduce pain, swelling, and tenderness, restore flexibility, and prevent recurrence, allowing comfortable movement and long-term relief.
"Correct alignment today protects your joints tomorrow.”
This both condition differ mainly in how the knees align and distribute body weight.
In genu valgum, the knees angle inward and touch while the ankles stay apart, causing increased stress on the outer knee, ankle, and foot, often associated with inward hip rotation and flat feet. In contrast, genu varum causes the legs to curve outward so the knees remain apart even when the feet are together, leading to greater load on the inner knee and hip, commonly linked with outward hip rotation and higher foot arches.
Both conditions alter gait and posture, increase joint stress, and may lead to pain or early degenerative changes if not biomechanically corrected.
Role of Rope & Belt Therapy – Strategic Joint Correction
Rope & Belt Therapy is a non-invasive osteo-rehabilitative technique used to guide the body into correct biomechanical alignment.
🔬 How It Works Biomechanically
- Applies controlled positional correction to hips, knees, and ankles
- Supports weight-bearing axis realignment
- Allows gentle joint decompression and guided stretch.
- Enhances proprioceptive awareness and neuromuscular control.
🌟 Why This Matters
Both genu valgum and genu varum are not just cosmetic concerns — they are functional alignment disorders that influence posture, movement efficiency, and long-term joint health.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome is a common overuse condition where the thick connective tissue running along the outside of the thigh becomes tight, irritated, or inflamed, often due to repetitive flexion–extension movements, muscle imbalance, or biomechanical stress, leading to friction at the lateral knee during activity.
From an osteopathic view, this disrupts lower limb mechanics, hip–knee function, gait, and posture because the IT band works with muscles like the tensor fasciae latae and gluteals to stabilize the hip and knee. We address the root causes by releasing myofascial restrictions, restoring hip, knee, and pelvic alignment, improving muscular balance and flexibility, optimizing gait mechanics, and reducing pain while preventing recurrence through movement correction and strength support.
Conditions

Frozen Shoulder
Adhesive Capsulitis or Frozen Shoulder is mainly characterized by pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. The causative factor is usually
Frozen Shoulder
Adhesive Capsulitis or Frozen Shoulder is mainly characterized by pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. The causative factor is usually
How to manage

- Relieve pain & inflammation using Class 4 Laser to calm nerves and improve blood flow
- Repair damaged tissue with Shockwave & Matrix Rhythm Therapy to rebuild healthy fibers
- Restore joint movement through Osteopathic techniques that release stiffness and adhesions
- Prevent recurrence by correcting posture, nerve flow, and shoulder movement coordination
Shoulder problems heal best when addressed early. Delaying treatment can prolong pain and stiffness. Sudden or unexplained left-side shoulder pain may be cardiac in origin—urgent medical consultation is advised.
Meet Our Experts

Dr. Sanjeevani Joshi(PT)
Osteopath
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Fellowship in Osteopathy and Manipulative Technique (FOMT), Dehradun
- Diploma in Osteopathy, Ontario
- REASET Approach

Dr. AMISHA SHAH (PT)
Osteopath
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Fellowship in Osteopathy and Manipulative Technique (FOMT), Dehradun
- Diploma in Osteopathy, Ontario
- REASET Approach

Dr. Srushti Said(PT)
Consultant Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Fellowship in Osteopathy and Manipulative Technique (FOMT), Dehradun
- Fellowship in Neuromuscular Skeletal Techniques (FNMT), Dehradun
- Cranial and Visceral Osteopathy

Dr. Vinayak Shinde(PT)
Consultant Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Fellowship in Osteopathy and Manipulative Technique (FOMT), Dehradun
- REASET Approach

Dr. Shivani Neema(PT)
Osteopath
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Diploma in Osteopathy, Ontario

Dr. Vijay Thite(PT)
Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Basic Spine – I
- REASET Approach
- Cranial and Visceral Osteopathy

Dr. Payal Chavan(PT)
Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- REASET Approach

Dr. Anjali Jadhav(PT)
Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Certified in Advanced Bio-mechanical Corrections

Dr. Harendra Singh Chouhan(PT)
Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)
- Fellowship in Neuromuscular Skeletal Technique(Dheradun)

Dr. Vaishnavi Kadam(PT)
Physiotherapist
- B.P.Th (Bachelor of Physiotherapy)

Dr. Sonali Dhore(PT)
Physiotherapist
- M.P.Th (Masters in Physiotherapy - Sports and Rehabilitation)
